OUR CHALLENGE
Emergency Planning
MARCH 3, 2025
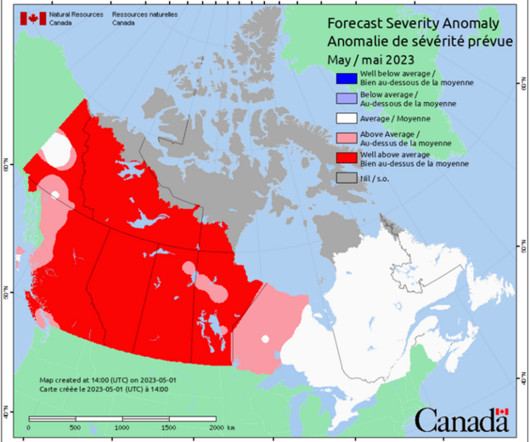
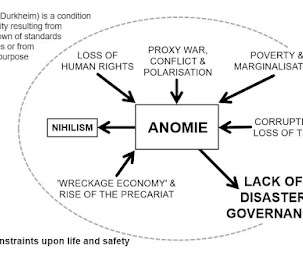
Emergency planning excluded emergency planners and was put in the hands of a consortium of medical doctors and politicians, yet half the battle in a pandemic is to manage the logistical, social and economic consequences. Natural hazard impacts are becoming fiercer, more extensive and more frequent.























Let's personalize your content