OUR CHALLENGE
Emergency Planning
MARCH 3, 2025
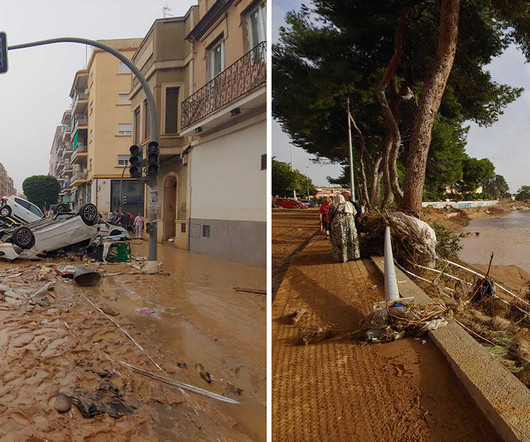
There have recently been some natural hazard events of extraordinary size and power, but they are no more than curtain raisers. Natural hazard impacts are becoming fiercer, more extensive and more frequent. We must also grapple with complexity and intersection with other forms of threat and hazard.



















































Let's personalize your content