AI for Wildfires and Heatwaves
National Center for Disaster Prepardness
JUNE 24, 2025
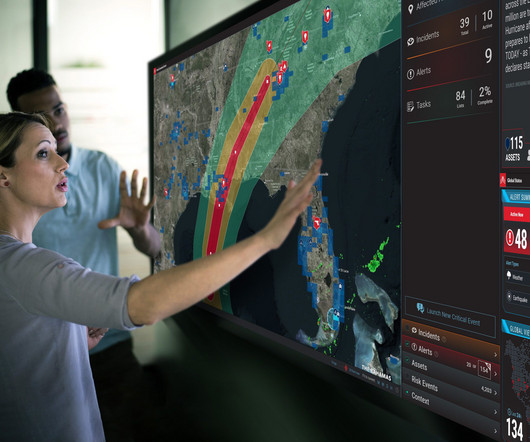
The 2025 wildfire season in the United States is forecasted to be above normal, highlighting the need to leverage emerging technologies for hazard risk mitigation. The Euro-Mediterranean and North African region MedEWSa serves is highly populated, economically vital, and rapidly warming, with a high diversity of people and hazards.


















Let's personalize your content