OUR CHALLENGE
Emergency Planning
MARCH 3, 2025
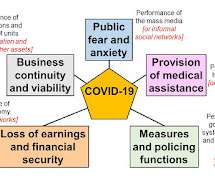
On 12th October 2008 I attended a conference at which an epidemiologist stood up and said "My job is to tell you something you don't want to know, and ask you to spend money you haven't got on something you don't think is going to happen." I taught pandemic preparedness on the basis of his example for the next 12 years.












Let's personalize your content